NetSuite's Script and Deployment Records
Created: September 17, 2017
In order for NetSuite to know how to utilize our SuiteScript source code, we need to be able to tell it which functions to call, when to call them, and who to call them for. We accomplish all of these with the Script and Script Deployment records.
Script Records
NetSuite uses the Script record to map the function(s) in your source file to specific events that occur in the system. For instance, if you need some business logic to run when a form is saved in the UI, the Script record will tell NetSuite which function to call when the saveRecord event occurs.
You can think of the Script record as defining when our source code should run; it essentially defines something akin to:
When a record is saved, call the
saveRecordfunction inhello-world.js.
Here is an example of what that Script record would look like:

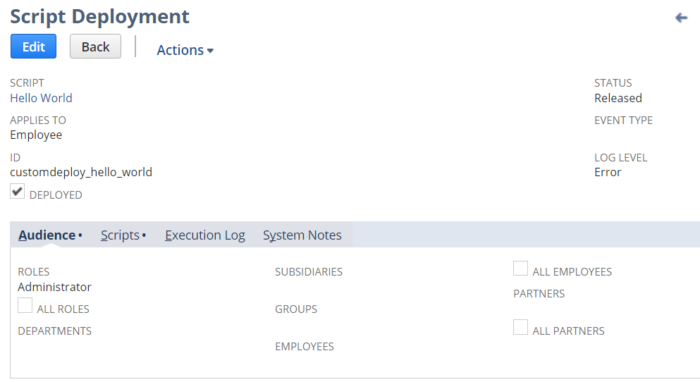
Script Deployment Records
Once we have a Script record created, we then need to deploy that script into the system. While the Script record tells NetSuite which functions to call from our source file, the Script Deployment record lets NetSuite know which records and users our Script should execute for.
While the Script record defines when our source code should run, the Script Deployment defines where and who can run our script. If we have a Script record that says:
When a record is saved, call the
saveRecordfunction inhello-world.js.
then our Script Deployment for that record might modify that slightly to:
When an Employee record is saved, call the
saveRecordfunction inhello-world.js, but only for users in the Administrators group.
Again, here is an example of what that Script Deployment would look like: